Ancient Greece and Rome are two of the most influential civilizations in history. They both left lasting legacies in various areas such as economy, culture, and military power. Rome is often celebrated for its advanced economy, which thrived on agriculture and trade, while Greece’s economic contributions are quietly noted through archaeological findings. Greek culture, with its myriad of philosophical and artistic achievements, deeply influenced Roman ideas, although Rome developed its unique artistic expressions as well.
Both civilizations had remarkable leaders who shaped their historical trajectories. Rome’s legacy includes its military prowess and extensive territorial expansion, while Greece is known for its influential thinkers and democratic ideas. Together, these civilizations shaped the foundations of Western thought and governance, leaving a rich tapestry of achievements that continue to fascinate scholars and history enthusiasts alike.
Key Takeaways
- Rome had a more advanced economy compared to Greece.
- Greek innovations and thinkers left a lasting impact on science and philosophy.
- Roman military power and leadership were unmatched in their era.
Comparing Ancient Societies
Rome Compared to Greece
Economy
The Roman economy was likely the most advanced in ancient Eurasia. Details are hazy, but trade expanded significantly during the Republic period, making important goods accessible. Rome used its vast territories for large-scale agriculture, which contributed to wealth and allowed the construction of luxurious villas. The economy also relied heavily on slavery, as conquered peoples were often forced to work the land. Conversely, the Greek economy is less understood. It also traded in commodities like wine and oil. Greece’s rocky soil made it less agriculturally productive, relying instead on colonies for resources. Evidence suggests Rome had a more sophisticated economy.
Ingenuity
Greece is celebrated for its contributions to science and philosophy. Greek thinkers advanced astronomy, mathematics, and even had early ideas about atoms. Innovations like cartography, hydraulics, and the Antikythera mechanism were pivotal. Their early rail system and use of aqueducts showcased their engineering skills. Rome, on the other hand, was renowned for its extensive road networks, which supported its empire’s vast expanse. The durability of Roman concrete contributed to the longevity of their structures. While Rome’s advancements were impressive, Greek ingenuity still influences modern times.
Leadership
Roman governance spanned over two millennia, featuring noteworthy leaders during both the Republic and Empire eras. They practiced democracy and occasionally implemented dictatorships in times of crisis. Leaders like Marcus Aurelius and Constantine the Great played vital roles in Rome’s resilience and evolution. Though not an empire, Greece saw leaders like Alexander the Great, who expanded his empire far beyond its origins. Other influential figures included Pericles and the father of democracy, Cleisthenes. Rome had numerous influential leaders throughout its history.
Culture
Greek culture left a lasting impact on the world, especially through mythology and architecture. Greek myths informed many aspects of Roman culture, which heavily borrowed the same stories and deities. Philosophy, spearheaded by figures like Aristotle, Plato, and Socrates, originated in Greece. Literary contributions and the Olympic Games are significant cultural landmarks. Romans embraced Greek culture but developed their unique art forms, such as mosaics and frescoes. The Latin alphabet’s development in Rome also stands out, along with gladiatorial events that remain iconic. Greek cultural influence was foundational for Rome and beyond.
Military
Rome’s military prowess is renowned, with its empire stretching across a vast territory. The legendary Roman legions and powerful naval forces underpinned its success in many campaigns. Greece, while militarized, often engaged in internal conflicts among its city-states. The Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta highlights Greek military involvement. Sparta’s reputation as a warrior society stands out, but Greek military achievements are less celebrated compared to Rome’s global impact.
Round One: The Economies
Rome’s Advanced Trade and Production
Rome’s economy was one of the most developed in ancient Eurasia. Though many daily details are lost, Rome’s vast expansion during the Republic period opened up numerous trade opportunities. Roman citizens benefited greatly, gaining access to important goods. The extensive territories Rome acquired were crucial for large-scale agricultural work. This expansion allowed many to become wealthy, trading in commodities like wine while constructing grand homes.
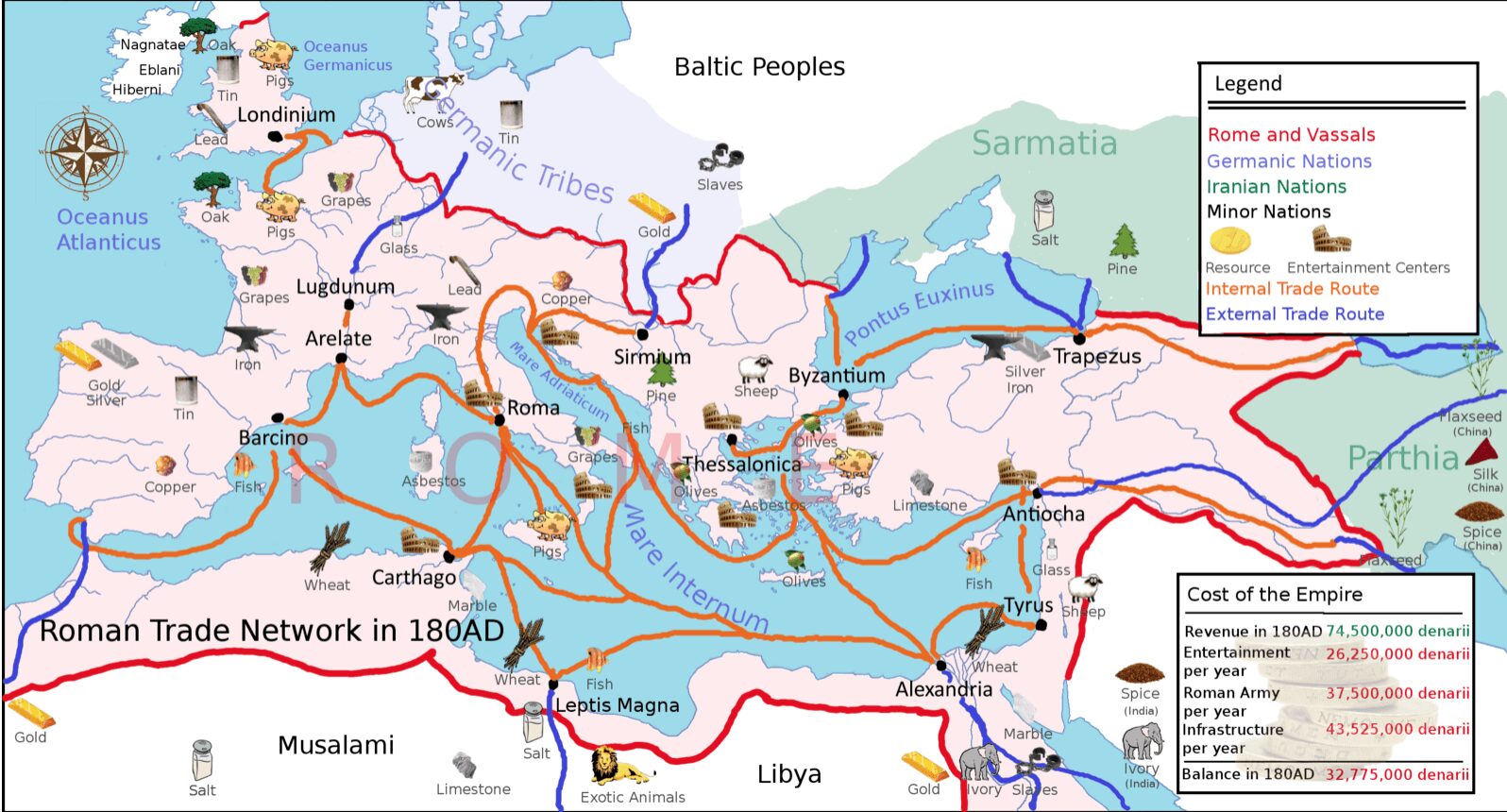
Farming and Forced Labor in Rome
Agriculture played a key role in Rome’s economic growth. Unfortunately, this growth came heavily at the expense of enslaved individuals. Many people from conquered regions were forced to work the land under Roman rule. This reliance on slavery fueled the economy, resulting in enormous wealth for some citizens.
Wealth and Trade in Ancient Greece
The economic landscape of ancient Greece was more mysterious and likely less advanced compared to Rome. Greece was known for trading in wine and oil, with evidence of this coming from pottery containers found throughout archaeological sites. While agriculture was present, Greece’s poor soil quality hindered its potential to dominate as an agricultural powerhouse like Rome.
Greek Commerce and Exchange
Greece leaned on its smaller colonies for resources, which were vital in its trade endeavors. This enabled Greece to engage in trade, though it’s hard to pinpoint the full range of goods they exchanged due to limited archaeological evidence. Still, Greece’s economic activities played a role in sustaining its city-states.
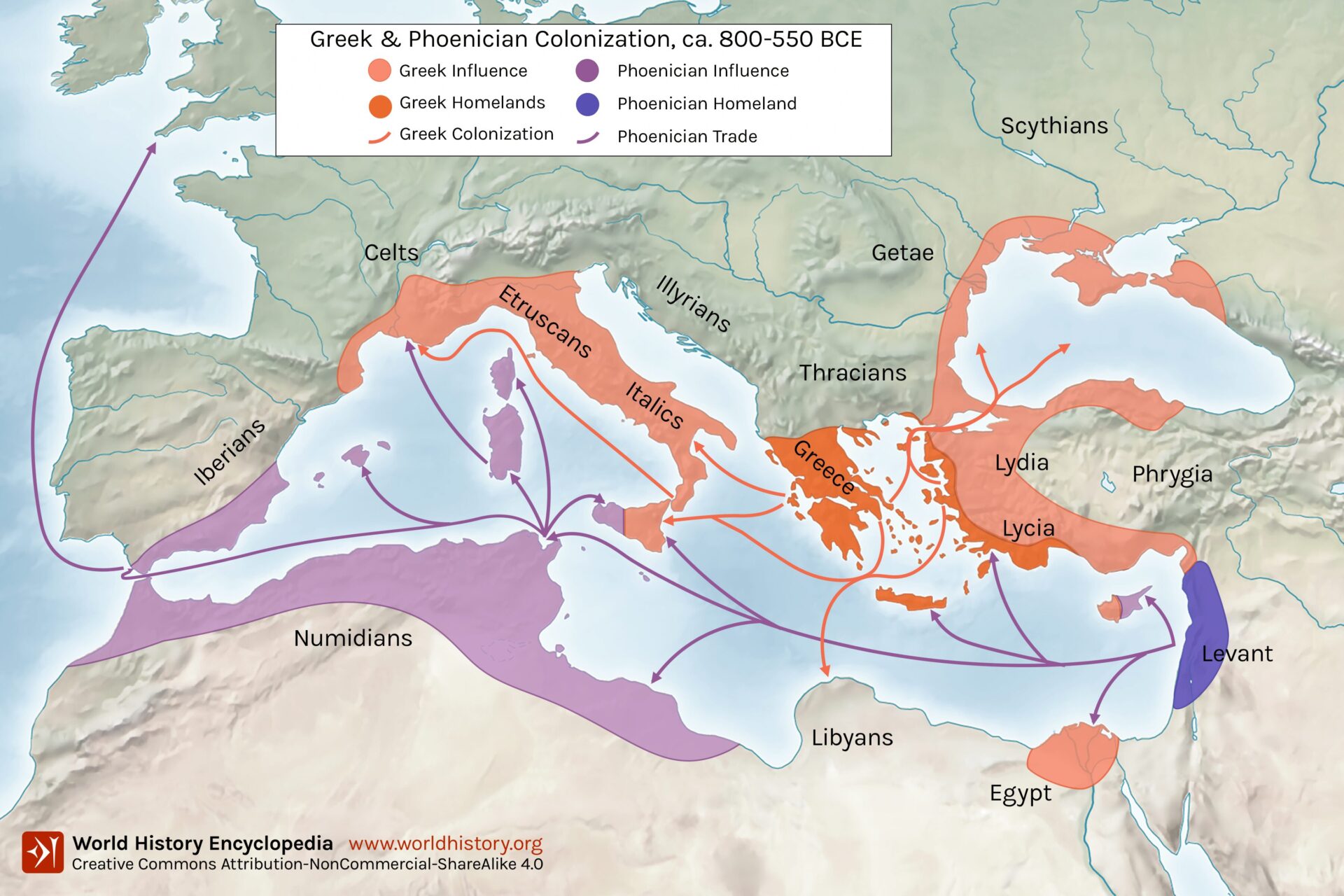
Triumph of Roman Efficiency
Despite Greece’s rich trade history, the evidence available points to the Romans having a more sophisticated and extensive economic system. With their advanced trade networks and agricultural practices, Rome established a dominant economic structure that surpassed its Greek counterparts.
Second Round: Creativity
Greece’s Intellectual Triumphs
Ancient Greece is famous for its impressive thinkers. The Greeks made great progress in many early fields of science, such as astronomy and mathematics. They even developed ideas about particles that are similar to today’s physics. Greeks were also responsible for early forms of maps and water systems. Notably, they created an ancient computing device known as the Antikythera mechanism, used for tracking celestial movements.

Stories of Archimedes
One of the most famous Greek inventors is Archimedes. There are fascinating tales about him, including a story where he supposedly used the sun’s rays to set enemy ships on fire. While modern experiments haven’t replicated this feat, Archimedes remains a legendary figure in history for his groundbreaking ideas and inventions.
Rome’s Lasting Roads
Rome is well-known for its long-lasting roads. These roads weren’t just simple paths but extensive networks designed to connect the vast reaches of the Roman Empire. Built with exceptional skill, many Roman roads are still used in Europe today. Such infrastructure showed Rome’s remarkable planning and construction abilities, helping maintain their empire’s connectivity.
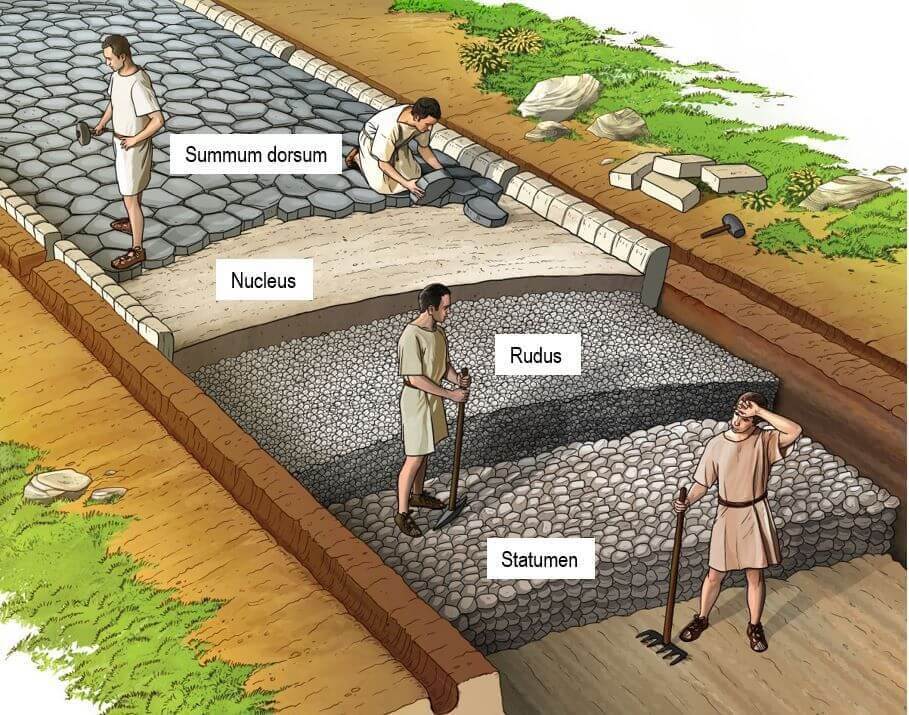
Roman Building Techniques
When it comes to construction, Roman methods were ahead of their time. They invented a special kind of concrete, the formulation of which was lost for many years. This concrete allowed their buildings to endure for centuries, and many Roman structures remain intact today. This incredible engineering legacy highlights the Romans’ skill in construction.
Greece’s Innovation Win
Greece’s contributions to the world through innovation are difficult to overlook. Many elements of Greek ingenuity are still relevant and applied today. Their advancements in science, technology, and philosophy have left a mark that proves their creative prowess, earning them recognition for their pioneering spirit.
Round Three: Influential Figures
Alexander of Macedonia and Greek Leaders
Alexander of Macedonia was a legendary military figure who led Greece to enormous victories, expanding its reach from Northern Africa to India. Under his guidance, Greece achieved a peak moment with widespread admiration. Greece had other remarkable figures like Pericles, who was instrumental during the battles against the Spartans, and Cleisthenes, renowned for advocating democratic ideas in Athens.
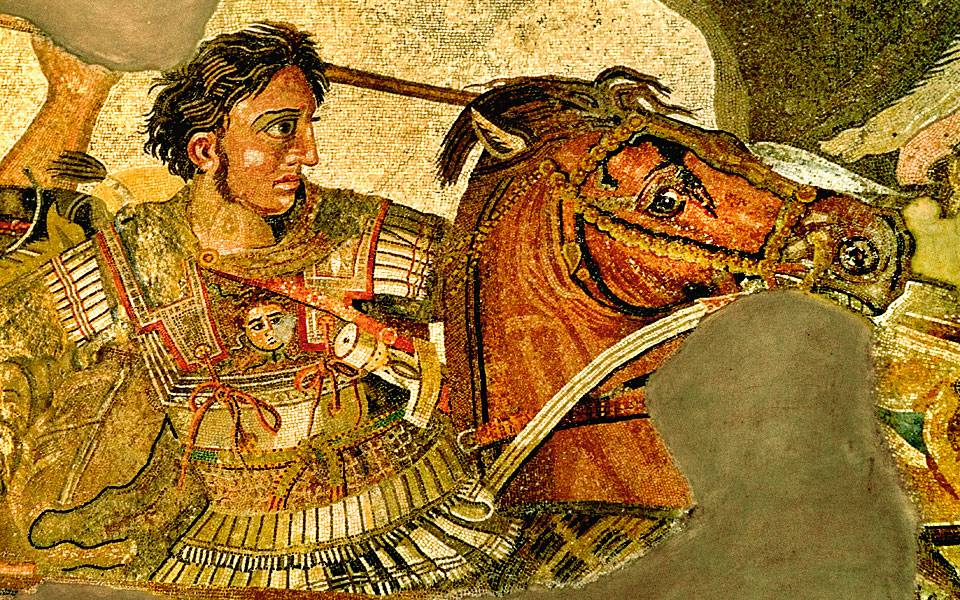

Greek Democratic Ideas
Greece is notable for its early embrace of democratic concepts, particularly in Athens. Leaders like Cleisthenes laid the groundwork for governance by the people, a contrast to the different systems seen elsewhere in ancient times. This set a precedent for later political systems, influencing the development of Western thought.
Roman Political Framework
In Rome, during the prolonged Republic era, a form of democracy existed that included the strategic use of dictatorships during crises. This approach allowed the Roman Republic to navigate numerous challenges effectively, laying a foundation for the vast Roman Empire. Dictatorship was a temporary measure, showing Rome’s flexible political structure.
The Rule of Emperor Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius was a Roman ruler in the 2nd century recognized as both a military leader and a stoic thinker. He defended Rome against numerous threats and is remembered as a philosopher king. His leadership exemplified wisdom and strength, integral to Rome’s enduring influence.

Dominant Authority of Rome’s Leadership
Rome had numerous influential leaders, with monumental figures like Constantine, known for adopting Christianity and enacting reforms that prolonged the Eastern Roman Empire. This ensured Rome’s lasting impact through centuries. The breadth of strong leadership underpins Rome’s historical success, showcasing why it often prevailed in historical comparisons.
Round Four: Cultural Contributions
Legends and Wisdom from Ancient Greece
Greek mythology has spread its influence throughout the world. Many of their myths remain well-known today, with stories of gods like Zeus and Athena fascinating people across generations. Besides myths, Greece is also home to many philosophers such as Aristotle, Plato, and Socrates. Their ideas formed the basis of Western thought and continue to be studied worldwide.
Greek Stories and Olympic Beginnings
Greek literature includes epic tales like those of Homer and dramatic plays by Sophocles. These narratives brought life to Greek myths. Greece also introduced the Olympic Games, a tradition that showcases athletic skills and fosters unity among diverse cultures.

Rome’s Artistic Spectrum
Roman art is noted for its rich variety, including intricate mosaics and vivid frescoes that adorned buildings. Roman creativity expanded beyond visual arts to include architecture, leading to iconic structures like the Colosseum.
Rome’s Letters and Arena Battles
The Latin alphabet, evolving in Rome, has become the foundation of many modern languages. Gladiator contests, held in large arenas, were popular public spectacles showcasing combat skills and drawing large crowds.
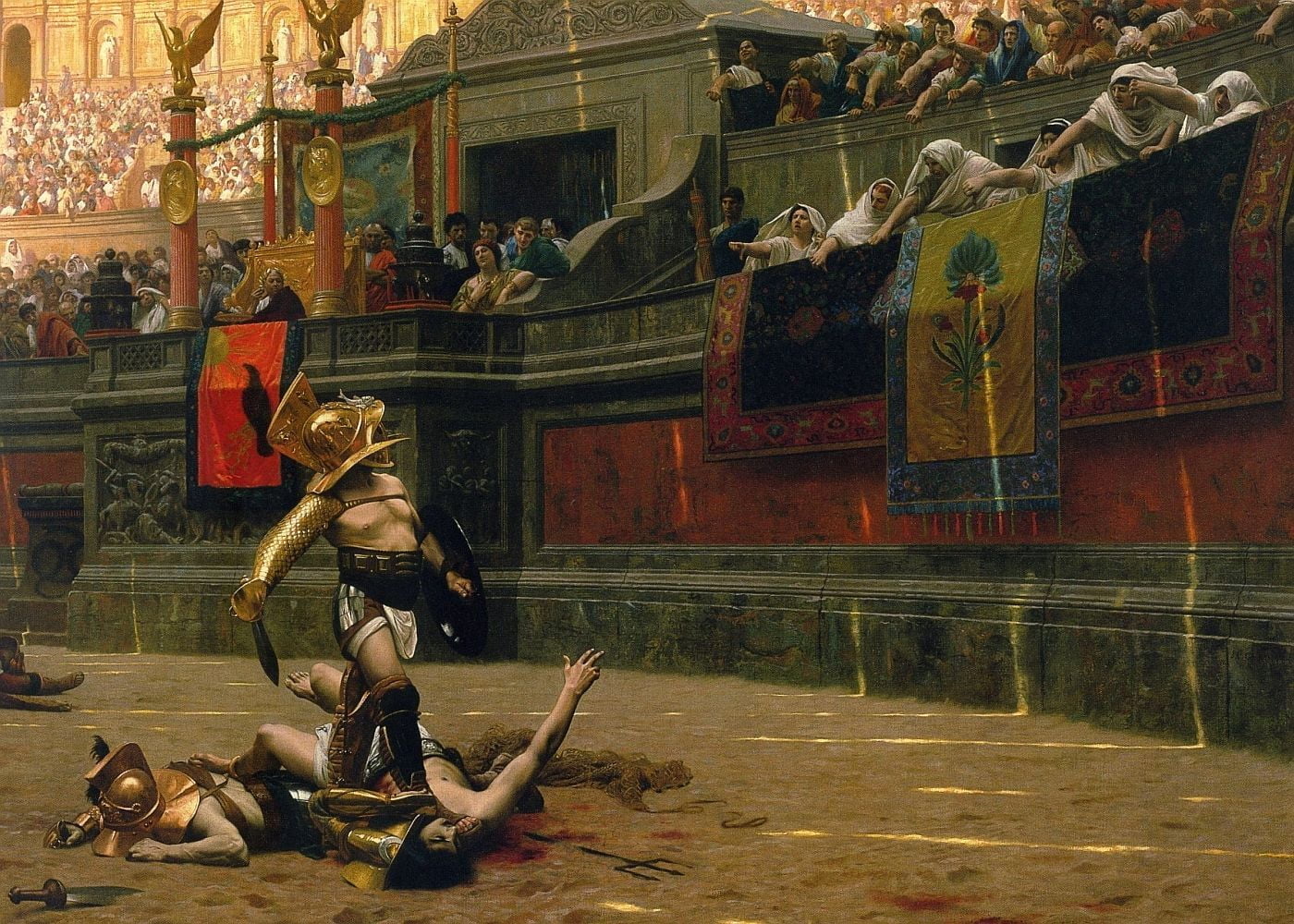

Honoring Cultural Impact
While both Greek and Roman cultures possessed their unique strengths, Greek culture laid foundational ideas that strongly influenced the Roman Empire’s development. This lasting impact is a testament to Greece’s significant contribution to the arts and philosophy.
Fifth Stage: Military
The Roman Military Engine
Rome is known for its incredible military power. Its army, organized into legions, was well-trained and numerous. These legions allowed Rome to win many battles and expand its empire across vast territories. Their military operations were precise and effective, contributing significantly to Rome’s dominance.

Sea Control and Growth
Rome’s naval forces played a crucial role in its expansion. The Mediterranean Sea was under Roman control, thanks to their large and powerful fleets. The navy was vital for Augustus when he founded the Roman Empire, ensuring safe passage and successful campaigns across the waters.
Conflicts in Greece
Ancient Greece saw frequent conflicts, not just against foreign enemies but also among its own city-states. These internal battles often involved powerful war fleets and armies, particularly during the prolonged Peloponnesian War between Athens and Sparta. The Greek capacity for war was evident, even if their focus was more internal.
Sparta’s Soldier Society
Sparta stands out as a society centered around warriors. The Spartans were trained to be strong fighters from a young age, making them a formidable force even by today’s standards. While they faced challenges, such as their battles against Xerxes, Sparta’s martial reputation has endured through history.

Recognition of Military Strength
Though Greece had its share of military capabilities, including legendary Spartan warriors, the scale and organization of Roman military might are often highlighted in history. Rome’s strategies and tactics left a lasting mark on military tradition, showcasing their excellence in warfare across the ancient world.
Closing Thoughts
The Legacy of Rome
Rome left a strong mark on history with its vast network of roads. These roads connected distant parts of Rome’s empire, and many are still used in Europe today. Roman concrete also contributed to long-lasting structures that stand even now.
Ancient Greece’s Long-Lasting Influence
Ancient Greece gave the world many important innovations. They had advanced ideas in astronomy and mathematics and were home to the earliest known computer, the Antikythera mechanism. Greek ideas about the atom mirror modern scientific thoughts today. Ancient Greek thinkers like Aristotle and Socrates laid the foundations for Western philosophy. Greek art, literature, and mythology continue to inspire people across the world.
