The Roman Empire left an indelible mark on history with its expansive reach and influence. At its height, it encompassed a substantial portion of the world’s population. The empire excelled in technology, governance, production, and military strength, unmatched by most other civilizations of the time, except for China. Roman citizens enjoyed a higher standard of living, benefiting from amenities that surpassed other societies. To understand the economic forces in Rome during the first two centuries A.D., it is important to consider the available data and recognize its limitations.
By studying the economic landscape, one can gain insights into Rome’s economic scale, output, and class distinctions. The evidence is limited and sometimes biased, requiring careful interpretation. Historical records, like literature and government proclamations, offer clues but are often vague. Despite the challenges, an exploration of Rome’s complex market system, reliance on agriculture and slavery, and its trade networks reveals the empire’s economic sophistication. Understanding the market dynamics highlights how regions specialized in industries, enhancing efficiency and life quality for many Romans.
Key Takeaways
- The Roman Empire significantly influenced global history and set a high standard of living.
- Available economic data is limited, requiring careful analysis and cautious conclusions.
- Sophisticated market systems and specialization improved efficiency and Roman life quality.
Overview of the Roman Empire’s Economic Reach
Population and Influence
At its height, the Roman Empire controlled a massive portion of the world’s population. This empire extended its reach across vast territories, leading to significant influence over global cultures and economies. Roman society was structured in a way that citizens often enjoyed a higher standard of living compared to people in other regions. This contrast in living conditions was due in part to the empire’s extensive organization and control.
Key Highlights:
- The Roman Empire encompassed a large portion of the global population.
- Roman citizens experienced unusually high living standards for the time.
- The empire’s dominance led to significant cultural and economic influence worldwide.
Technological Progress and Government Structure
Roman advancements in technology and governance set it apart from its contemporaries. The organization of their government and military was sophisticated, enabling them to maintain control over such a large area. They also excelled in engineering and construction, creating infrastructure that supported the economy, like roads and aqueducts.
Important Points:
- The Roman government was complex and highly organized.
- Advancements in technology and infrastructure supported Roman dominance.
- Roman engineering feats contributed to economic success and societal well-being.
By providing a comprehensive examination of population dynamics and technological progress, the Roman Empire showcased its capability to affect economic conditions significantly and leave a lasting mark on history.
Comparing Lifestyle Standards
Income Levels and Utility Access
During the peak of the Roman Empire, the typical Roman citizen enjoyed a lifestyle far advanced compared to other societies of the time. People had access to various public utilities, which was uncommon elsewhere. Romans experienced a standard of living that provided amenities and benefits not seen again until much later in human history.
Access to public services was a distinct feature of Roman life, contributing to the quality of life. These services included public baths, water supply systems, and well-maintained roads, which facilitated easier travel and trade.
Echoes of Modern Economies
The Roman economic structure featured a market system that was both complex and interconnected, similar to modern economies today. This market allowed different regions within the empire to specialize in certain industries, boosting efficiency and productivity. Such specialization was evident in trade, as different parts of the empire produced items they could make best and traded for things they needed.
The prevalence of trade and market transactions in the Roman Empire’s first two centuries showcases an economic integration that fostered a high quality of life for its citizens. This complex economy provided advantages that resonated with some aspects of current economic systems.
Sources of Economic Data and Their Constraints
Limited Evidence and Difficulties
Finding solid data about the Roman economy is a real challenge. The records are few, incomplete, and sometimes changed or made up. Historians usually avoid studying the details of how Rome’s economy worked. When they do try, different studies often come to different conclusions. Written records from the time are not very reliable because they might exaggerate or be used to influence people.
Most of the evidence we have doesn’t come from direct sources. Instead, historians look at writings from that time, official statements carved in stone, findings from digs, and ancient Egyptian writings that survived in dry places. Other less direct clues come from things like shipwrecks or ice layers that show historical carbon dioxide levels.
Applying Ancient Economic Concepts
Even with these challenges, some broad ideas about the Roman economy can be formed. Studies in old economic history help, but any conclusions made are usually careful and have limits. Economic interactions such as sales or loans were recorded on wood covered with wax, which didn’t last long, adding to the difficulty in getting accurate information.
Using the available data, people can make guesses about Rome’s economy at a larger level. From this, the size of the economy, the different social and money-related classes, and the real-life conditions of the people can be studied. Although caution is always important, considering these findings next to today’s economies gives a glimpse into ancient economic systems and their impact.
Evaluating the Economy’s Magnitude and Production
Social Economic Division Analysis
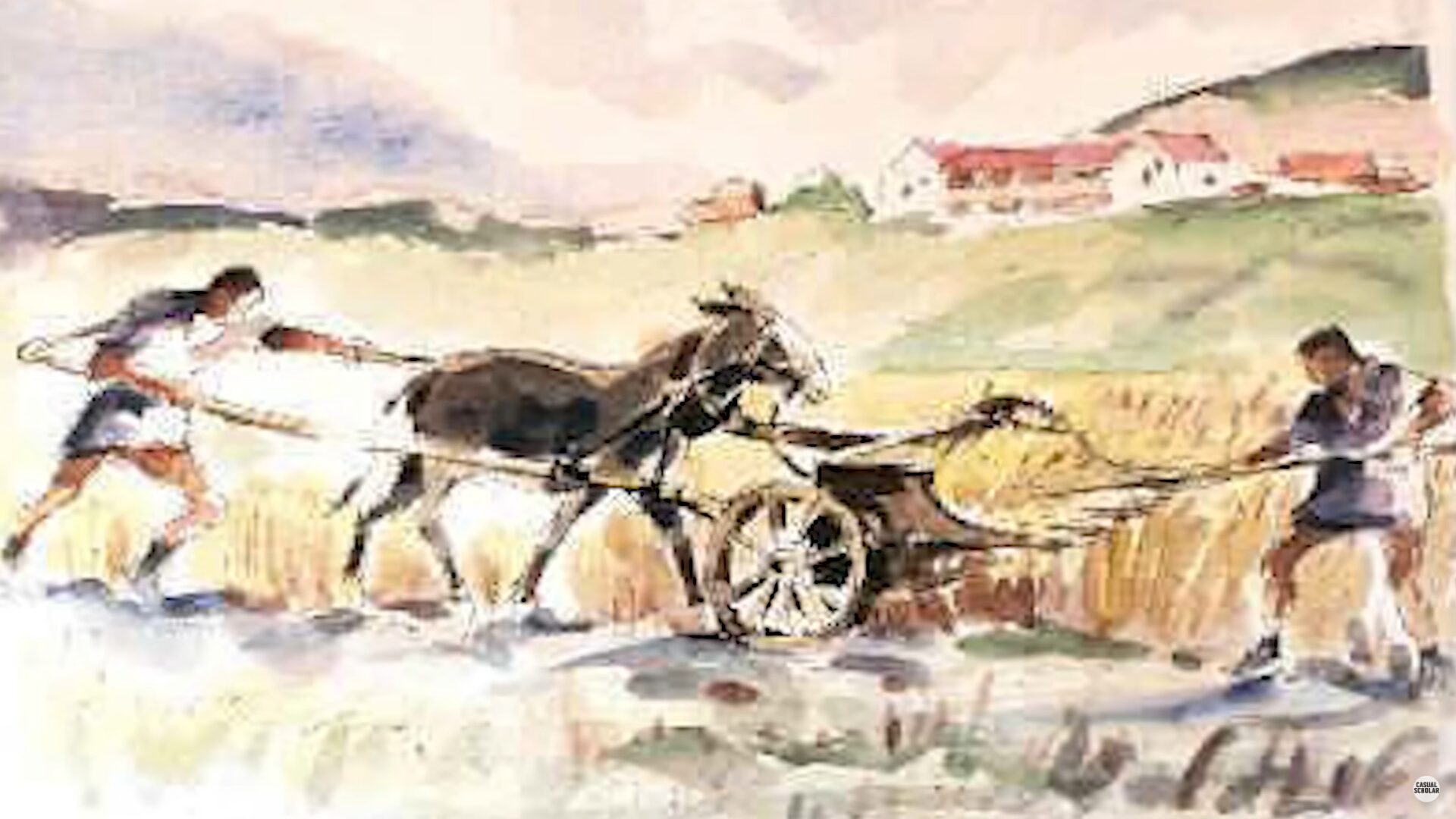
In the Roman Empire, the distribution of wealth and societal roles was clear yet diverse. The empire was predominantly rural, with roughly 90% of people living in the countryside, often working in agriculture. A significant segment of this population was enslaved, serving various functions from farming to skilled trades like medicine or accounting. Enslavement was not always a life sentence; some slaves could earn freedom and become full members of society.
Despite the heavy reliance on slavery, the Roman economy was not the most dependent on enslaved labor compared to other ancient civilizations. Enslavement in Rome had an openness not seen in other societies, allowing for the possibility of social mobility. Slaves played an essential role in supporting the upper classes and state functions through hard work in demanding roles.
Evaluation of Living Conditions
The Roman Empire was noteworthy for its high living standards during its peak. Citizens enjoyed amenities and public utilities uncommon in other parts of the world during that era. This level of comfort was due in part to a well-integrated market economy that facilitated trade and specialization across different regions of the empire.
Roman markets operated independently of central government interference, running on natural supply and demand forces. This system enabled economic growth and increased productivity as regions within the empire specialized in particular trades or industries. Comparative advantages were utilized, enhancing the quality and efficiency of goods, which in turn contributed to a relatively high quality of life for its citizens. These conditions set a precedent for living standards that would not be surpassed until the development of modern economies in the 17th century.

Risks and Limits Analysis
Notable Financial Drawbacks
The Roman Empire’s economy had several weaknesses. To start, most people in the empire relied heavily on agriculture. About 90% of Romans lived in rural areas, working on farms or in related jobs. This dependence on farming made the economy fragile and vulnerable to factors like crop failures and poor harvests.
Additionally, slavery played a big part in the economy. Many laborers were slaves, which affected economic dynamics. Though some slaves had skills, most were involved in demanding manual labor. This reliance on slave labor raised ethical concerns and might have hindered economic development.
Insights from Current Economic Structures
Learning from the past, modern economies can identify areas for improvement. While the Roman market system was broad and relatively advanced, our systems have evolved to be more inclusive and diverse. In contrast to ancient times, today’s economies benefit from technological advancement and more efficient resource distribution.
The Roman economy operated largely outside central government control. Understanding its self-regulating nature can guide modern economies to balance regulation with freedom. By fostering open markets and specialization, as seen in the Roman Empire, countries could boost productivity and improve living standards.
In the future, building sustainable economies requires learning from Rome’s shortcomings and strengths. Balancing agricultural reliance, labor practices, and market integration could help create more stable and robust systems globally.
Historical Records and Their Flaws
Limited Evidence and Prejudices
When studying the Roman Empire, a major challenge is the lack of direct evidence. Most existing historical documents either provide minimal detail or exhibit clear biases. For instance, there’s only one Roman shield still in good shape today. In the realm of economic data, plenty of transactions were once noted by traders using wax tablets, but these records have mostly perished over time. Because of this, historians often rely on indirect sources, such as ancient literature, formal decrees, and archaeological findings. Each of these sources has its own issues, whether it’s exaggeration or the difficulties of interpretation.
Difficulties in Understanding Written Documents
Written sources from the Roman times are often problematic. Many are filled with exaggerations, serving more as propaganda rather than reliable records. Writers sometimes spruced up facts to make rulers or projects appear more impressive. One example is the Mazeros Papyrus, which details a maritime loan. The papyrus’s poor grammar suggests that such loans were routine, so records were made quickly without much concern for accuracy. Beyond business documents, the structural elegance of buildings and other long-lasting artifacts also provides insights into the era. All these data sources together form a patchwork of information, but they come with a host of limitations that must be carefully considered.
Different Methods for Evaluating Economic Proof
Categories of Indirect Proof
Examining the economy of the Roman Empire presents a challenge due to the lack of direct records. Instead, researchers rely on four main types of indirect evidence.
Literature: Ancient writings sometimes include vague references that shed light on economic conditions.
Government Decrees: These are inscribed on stone and often contain broad statements, occasionally overstated.
Archaeology: Archaeological discoveries provide clues about trade, infrastructure, and material goods.
Preserved Documents: Egyptian papyri, surviving in dry climates, offer additional insights.
Collectively, these sources form the basis for understanding ancient economic systems, despite their limitations.
Use of Ancient Mediterranean Shipwrecks
Another innovative approach involves studying ancient shipwrecks in the Mediterranean. These underwater sites reveal trade routes and the frequency of maritime commerce. The number of wrecks found can indicate periods of economic activity and trade volume. Each shipwreck offers a snapshot of the goods traded and the economic connections between regions. This method, paired with other evidence, helps to recreate a more complete picture of the Roman economic environment.

Economic Foundations of Early Rome
Farming and Forced Labor
The economy of early Rome heavily relied on agriculture and the use of forced labor. About 90% of the people lived in rural areas, with their primary occupation being farming or jobs related to agriculture. A significant portion of this rural population were slaves, making up about 10% to 20%. These slaves, acquired through birth, capture, or punishment, were considered the property of the state. Unlike the harsh slavery seen in later history, Roman slavery offered some slaves the chance for freedom and integration into society.
Slaves in Rome were mainly tasked with hard labor such as farming, construction, or serving as domestics. Some, however, possessed skills and worked as physicians or accountants. The majority of these individuals endured demanding work that benefited the ruling class. Although dependent on forced labor, Rome was not the most reliant on slaves among ancient economies. For example, in Sparta, the slave population far exceeded that of the Spartans.
Countryside Inhabitants and Slave Interactions
In the Roman countryside, life revolved around farming, with most people living off the land. The population dynamics were impacted significantly by slavery. Slaves played a crucial role, performing the majority of the labor-intensive tasks. Despite their crucial role, not all slaves remained in servitude. Some obtained freedom and, upon release, were fully accepted into Roman society.
This acceptance marked a difference from the rigid slave systems seen in other parts of history. However, a large number of slaves continued to live harsh lives, working in the fields or in domestic settings. Skilled slaves held positions as artisans, doctors, or in other specialized fields, contributing to the economy’s efficiency and sophistication. The debate continues among scholars regarding the exact dependency of the Roman economy on slave labor, but the influence was undeniably significant.
Economic System and Trade Connections
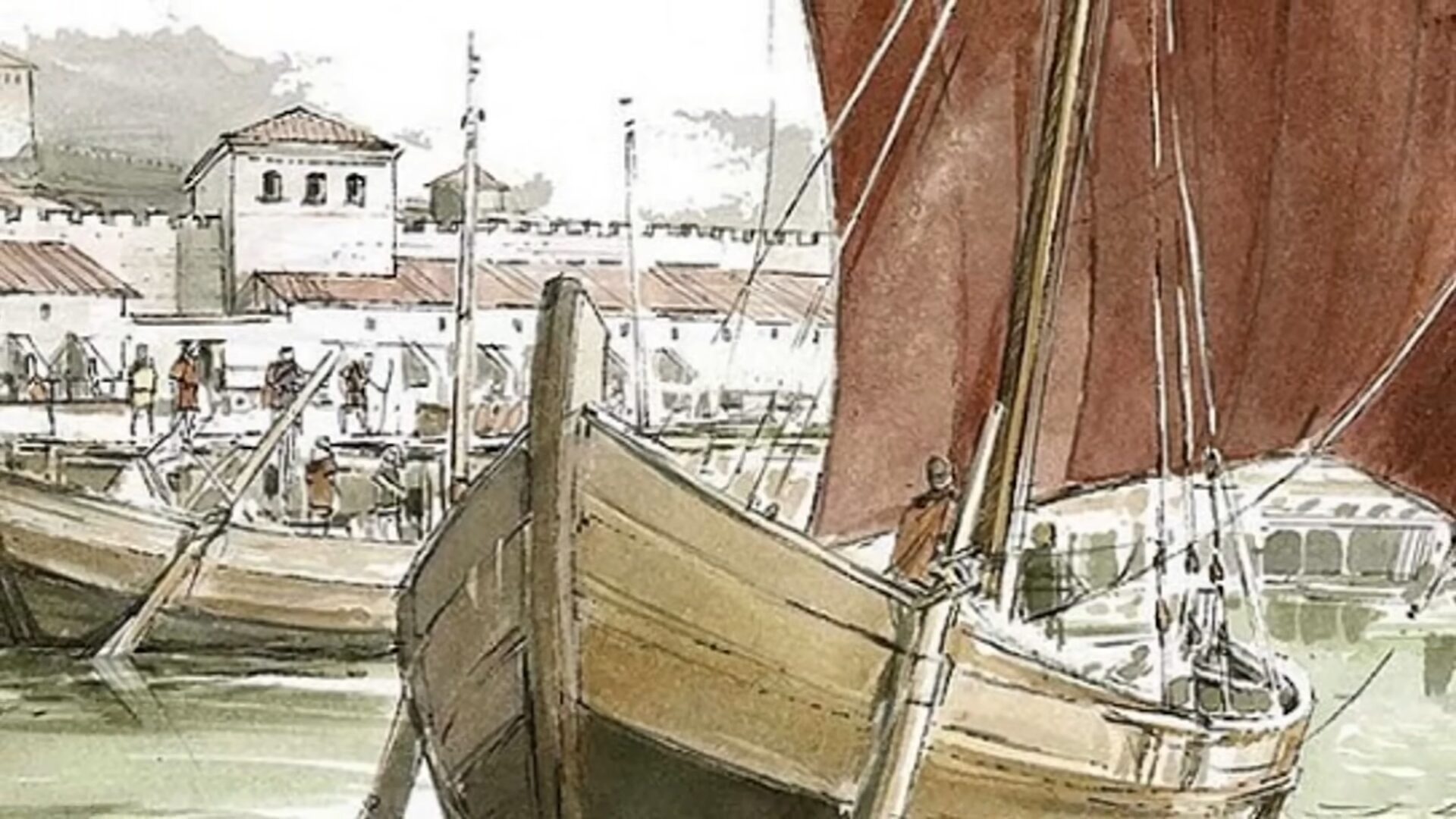
Supply and Demand in Natural Markets
In ancient Rome, markets operated with a natural balance of supply and demand. Most of the economy functioned independently of government control, allowing farmers, artisans, and merchants to engage in trade. Roman markets were bustling hubs where goods such as grain, olive oil, and pottery were exchanged. The forces of supply and demand helped set prices and ensured that a variety of goods were available. The vibrancy of these markets was central to the economic vitality of the Roman Empire.
Benefits and Special Focus Areas
Different regions within the Roman Empire became known for specific products, which enhanced efficiency and output. For example, certain areas excelled in producing wine, while others were famous for textiles. This specialization allowed regions to trade their best products with one another, increasing overall productivity. The system of specialized production and trade was a key factor in the empire’s ability to maintain a high standard of living. This integration of markets allowed for the use of comparative advantages, making the Roman economy a complex and successful organization.
Results of Market Intricacy
Influence on Living Standards
The Roman Empire’s markets played a crucial role in enhancing the living conditions of its citizens. The complex and well-integrated market system allowed for improved access to resources and goods. Citizens benefited from a range of public amenities and services that were unmatched by other societies at the time. This high standard of living was partly due to the effective use of regional specialties within the empire, creating an efficient and productive economy.
Growth of Trade in the Initial Two Centuries A.D.
Trade blossomed significantly during the first two centuries of the Roman Empire. The empire’s markets were not only vast but also sophisticated. This allowed different regions within the empire to specialize in specific industries, improving overall productivity. The thriving trade networks allowed for a steady flow of commodities and cultural exchanges, encouraging the growth of a robust economy. The trade routes facilitated connection between distant regions, enhancing economic stability and diversity.
