Trade was an essential aspect of the Roman Empire’s economy and played a significant role in its success and expansion. It played a key role in the development and prosperity of the ancient Roman world. From the bustling markets of Rome to the far-reaching trade routes that connected distant regions, commerce was a driving force in shaping the economic, social, and cultural landscape of the Roman Empire.
The Romans were known for their extensive trade networks that spanned across Europe, Asia, and Africa. Trade routes were established and maintained through the use of roads, rivers, and seas, allowing for the transportation of goods and resources.
The Roman economy was heavily reliant on trade, as it allowed for the exchange of goods, services, and ideas between different regions. The empire’s vast size and diverse population meant that there was a high demand for a variety of products, including food, textiles, metals, and luxury goods. The Roman government also played a role in regulating trade, establishing laws and policies to ensure fair trade practices and protect merchants and consumers. In general, trade was a crucial component of the Roman economy, contributing to its growth and prosperity.
Economic Foundations
Trade in Rome as the Romans did! The ancient Romans were not just conquerors but also clever merchants who participated in thriving trade routes that reached across continents. The Roman economy was based on agriculture and the production of goods such as pottery, textiles, and metals. However, the expansion of the empire led to the development of a more complex economy that relied on trade to sustain it.
It was the lifeblood of the Roman Empire, connecting distant lands and cultures, fueling economic growth, and bringing exotic goods to the markets of Rome. Without it, the Roman world would have been a lot less fabulous and a lot more boring.
The Roman economy was characterized by a high degree of specialization, with different regions producing specific goods. For example, the fertile lands of Egypt produced grain, while the province of Hispania produced wine and olive oil. Trade routes were developed to transport these goods throughout the empire, and the Roman government played an important role in regulating and protecting trade.
Political Climate
The political climate of the Roman Empire was also an important factor in the development of trade. The stability and security provided by the Roman government allowed for the establishment of trade routes that spanned the entire empire. The government also played a role in regulating trade, ensuring that goods were of high quality and that prices were fair.
However, there were certain challenges. Piracy was a significant problem in the Mediterranean, and the Roman government had to devote significant resources to combating it. Additionally, political instability in the empire could disrupt routes and lead to economic downturns.
Despite these challenges, trade played a crucial role in the Roman economy and helped to sustain the empire for centuries. The legacy of Roman trade can still be seen today in the products and technologies that were developed during this time period.
Trade Routes
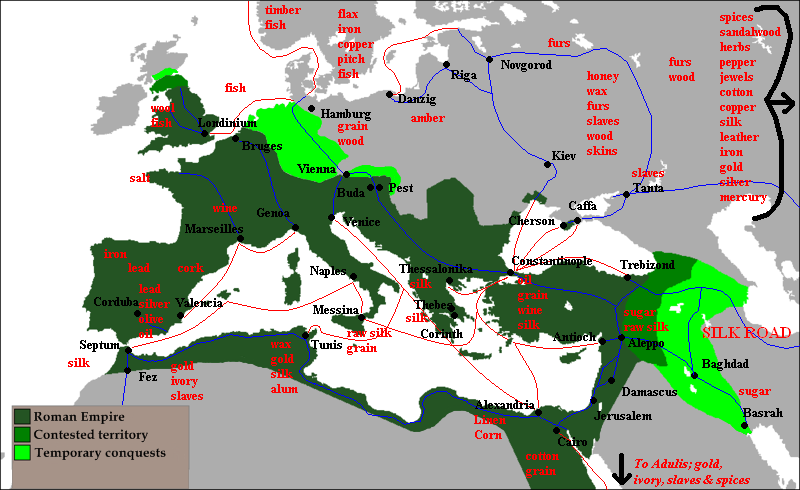
Via Maris
One of the most important routes in the Roman Empire was the Via Maris, also known as the “Way of the Sea.” This route connected Egypt, Syria, and Palestine to the eastern Mediterranean. It was a major route for the transportation of goods, including spices, silk, and precious metals. The route was also used for the transportation of troops and for communication between different regions of the empire.
Silk Road
The Romans didn’t just build roads for conquering – these roads were also crucial trade routes that connected the empire from Britannia to Egypt and beyond, facilitating the flow of goods and ideas. The Silk Road was a network of routes that connected the Roman Empire to China. The route was used for the transportation of silk, spices, and other luxury goods. It was named after the most famous commodity traded along the route – silk. The Silk Road was a vital link between the East and the West, and it played a crucial role in the development of the Roman Empire.
Amber Road
The Amber Road was a route that connected the Baltic Sea to the Adriatic Sea. It was named after the most valuable commodity traded along the route – amber. The route was used for the transportation of amber, furs, and other goods. The Amber Road was an important link between the Roman Empire and the northern regions of Europe. The Roman Empire had a vast network of trade routes that connected it to different regions of the world. These routes played a crucial role in the economic development of the empire and helped to spread its influence across the globe.
Commonly Traded Goods in Ancient Rome
From grain to wine, olive oil to pottery, the Romans traded in everyday essentials that kept their empire running smoothly. These goods were the bread and butter (or should we say, bread and olives?) of Roman trade. The Roman Empire was heavily reliant on grain imports, particularly from Egypt, to feed its population. Grain was a staple food for the majority of the population, and the government went to great lengths to ensure a steady supply. The state even established a grain dole, known as the ‘Annona,’ to provide free or subsidized grain to the poor.
In addition to grain, other provisions such as olive oil, wine, and salt were also important commodities in the Roman economy. Olive oil was used for cooking, lighting, and as a cosmetic, while wine was a popular luxury item. Salt was essential for preserving food and was widely traded throughout the empire.
Of course, the Romans weren’t satisfied with just the basics. They craved luxury and exotic goods like silk from China, spices from the East, and ivory from Africa. These fancy imports helped to solidify Rome’s reputation as a cosmopolitan and sophisticated society. The Roman elite were known for their lavish lifestyles and love of luxury goods. These goods were often imported via the Silk Road or by sea and were highly valued for their rarity and exoticism. Other luxury items included fine textiles, such as Egyptian cotton and Tyrian purple dye, as well as exotic animals, such as lions and elephants, which were used for entertainment and spectacle.
Raw materials such as metals, wood, and stone were also important commodities in the Roman Empire. Metals such as gold, silver, and copper were used for coinage, jewelry, and decorative objects. Wood was used for building, shipbuilding, and furniture, while stone was used for construction and sculpture.
The Roman Empire was also known for its mining operations, particularly in Spain, where large deposits of silver were found. Lead, tin, and iron were also mined throughout the empire, and were used for a variety of purposes, from plumbing to weaponry.
Monetary System
Trade wasn’t just about goods – it also shaped the Roman currency and markets. The abundance of coins from transactions led to developments in banking, and credit systems, and the rise of bustling marketplaces where goods of all kinds changed hands. It was like ancient Rome’s version of Wall Street, but with more togas and fewer suits.
The Roman Empire had a well-developed monetary system that played a crucial role in facilitating trade. The basic unit of currency was the denarius, which was made of silver and had a consistent weight and purity. The denarius was widely accepted throughout the empire and was used to pay soldiers, taxes, and for everyday transactions.
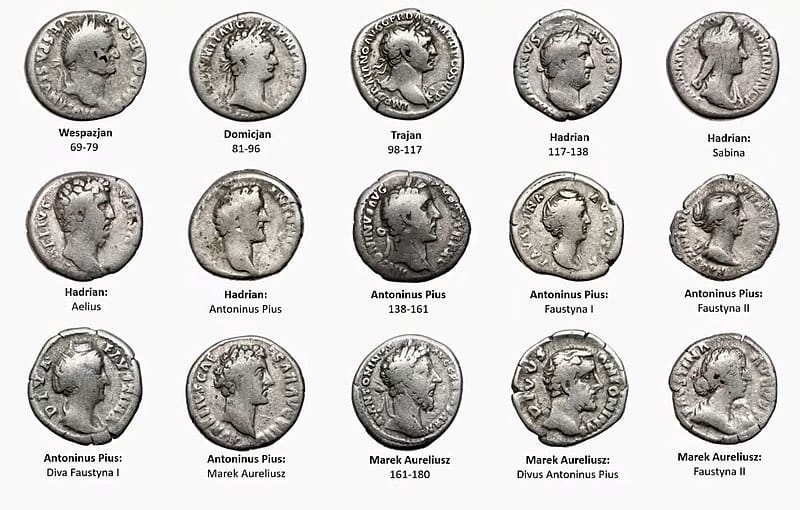

In addition to the denarius, the Roman Empire also minted other coins of varying denominations, such as the aureus, sestertius, and as. These coins were made of different metals and had different values, but they were all standardized and widely accepted.
Impact on Society and Culture
When it comes to trade in the Roman world, it wasn’t just about exchanging goods – it was also a cornerstone of society and culture. In the bustling world of Roman trade, you would find a mix of people from different social classes getting involved. From wealthy merchants to humble traders, trade played a crucial role in connecting people from all walks of life.
It wasn’t just about buying and selling goods, as it was a gateway to cultural exchange in the Roman Empire. As goods traveled along various routes, they carried not just commodities but also ideas, beliefs, and customs that enriched Roman society. There were rules, regulations, and guilds that governed how trade operated.
Influence on Global Trade Patterns
The expansive routes built by the Romans not only connected distant lands but also paved the way for future trade networks. The legacy of Roman routes can still be seen in today’s global trade patterns, showing how ancient commerce continues to shape the modern world. The networks of ancient Rome not only facilitated the exchange of goods but also served as conduits for the dissemination of ideas, technologies, and cultural influences across vast territories.
The legacy of Roman trade continues to resonate in contemporary global commerce, underscoring the enduring impact of commercial activities on society. From supply chains to currency systems, modern practices still bear the imprint of Roman commerce. The principles of fair trade, regulation, and market dynamics that the Romans established continue to shape the way we conduct business today.
People Also Ask:
What were the main routes in the Roman world?
There were several routes to the East. In the north, trade passed through the Caucasus, crossed the Caspian Sea, and then went up the Amu Darya (Oxus) river. Of much greater significance was the route from the Mediterranean through Damascus and the desert city of Palmyra to Mesopotamia.
How did trade impact the economy of ancient Rome?
Agriculture and trade contributed to the success of the Roman Empire. The Roman Empire provided a higher standard of living for its citizens by exporting (sending out) goods that it had too much of, like food products, and importing (bringing in) goods that it could not make or that it wanted for luxury.
What are 3 ways the Roman government involved itself in trade?
While the Roman army protected the routes on land, the navy made sure the sea routes remained safe for ships to travel. Rome also provided many lighthouses to ensure the safety of ships. In fact, Rome provided much of the security in order for it to be successful.
How has the Roman Empire influenced the modern world?
Though it has been thousands of years since the Roman Empire flourished, we can still see evidence of it in our art, architecture, technology, literature, language, and law. From bridges and stadiums to books and the words we hear every day, the ancient Romans have left their mark on our world.
Who made the first trade routes?
Throughout history, routes have played a vital role in shaping the world’s economic and cultural landscape. Today, numerous routes exist throughout the world, keeping societies running. But how did this all start? It began with one trade network during the Han Dynasty in China and lasted for 1,500 years.
Hello, my name is Vladimir, and I am a part of the Roman-empire writing team.
I am a historian, and history is an integral part of my life.
To be honest, while I was in school, I didn’t like history so how did I end up studying it? Well, for that, I have to thank history-based strategy PC games. Thank you so much, Europa Universalis IV, and thank you, Medieval Total War.
Since games made me fall in love with history, I completed bachelor studies at Filozofski Fakultet Niš, a part of the University of Niš. My bachelor’s thesis was about Julis Caesar. Soon, I completed my master’s studies at the same university.
For years now, I have been working as a teacher in a local elementary school, but my passion for writing isn’t fulfilled, so I decided to pursue that ambition online. There were a few gigs, but most of them were not history-related.
Then I stumbled upon roman-empire.com, and now I am a part of something bigger. No, I am not a part of the ancient Roman Empire but of a creative writing team where I have the freedom to write about whatever I want. Yes, even about Star Wars. Stay tuned for that.
Anyway, I am better at writing about Rome than writing about me. But if you would like to contact me for any reason, you can do it at [email protected]. Except for negative reviews, of course. 😀
Kind regards,
Vladimir
