The Roman Empire is often regarded as one of the most influential empires in history. Its impact on language is no exception. Latin, which was the official language of the Roman Empire, has had a significant influence on modern languages. In fact, Latin is still used today in various fields, such as law, medicine, and science.
During the Roman Empire, Latin served as a unifying language for the people of the empire. It was used in government, education, and everyday life. As the empire expanded, Latin spread throughout Europe and became the language of the Catholic Church. Latin also influenced the development of other languages, such as French, Spanish, and Italian. Today, many English words have Latin roots, making it an important part of the English language.
Latin: The Language of the Roman Empire
Latin was the official language of the Roman Empire and was widely spoken throughout the Mediterranean world. It was the language of government, law, and administration and was used in official documents, inscriptions, and religious ceremonies. Latin was also used in literature, philosophy, and science, and many of the greatest works of Western civilization were written in Latin.
The spread of Latin was facilitated by the expansion of the Roman Empire, which brought Latin-speaking people into contact with other cultures. As the Roman Empire grew, Latin became the dominant language of the Western world, and its influence can still be seen today in the many languages that are derived from it.
Latin was also the language of the Catholic Church, and the Latin Mass was celebrated until the Second Vatican Council in the 1960s. Latin remains important for scholars and scientists and is still taught in many schools and universities around the world.
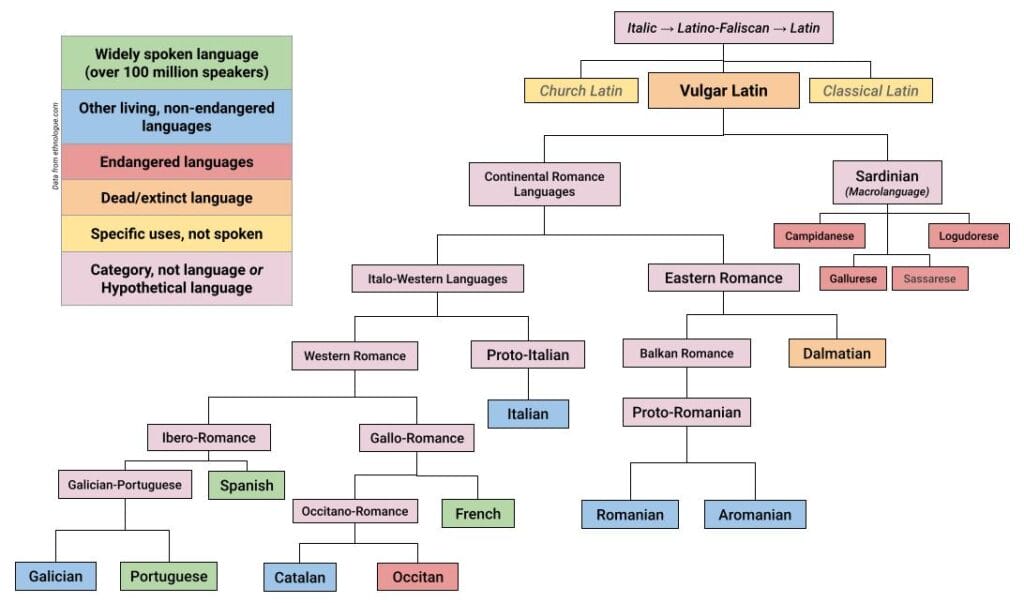
Linguistic Influence on Languages
Spanish
The influence of the Roman Empire on the Spanish language is evident in its vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. Spanish has borrowed many words from Latin, such as “casa” (house) and “amigo” (friend). The grammar of Spanish is also influenced by Latin, as it has retained many of the same verb conjugations and noun declensions. The pronunciation of Spanish has also been influenced by Latin, as the stress patterns and vowel sounds are similar.
French
French, like Spanish, has been heavily influenced by Latin. French is known for its complex grammar, which is similar to Latin. French has also borrowed many words from Latin, such as “maison” (house) and “ami” (friend). The pronunciation of French has also been influenced by Latin, as the stress patterns and vowel sounds are similar.
Italian
Italian has borrowed many words from Latin, such as “casa” (house) and “amico” (friend). The grammar of Italian is also influenced by Latin, as it has retained many of the same verb conjugations and noun declensions. The pronunciation of Italian has also been influenced by Latin, as the stress patterns and vowel sounds are similar. Yes, almost the same as Spanish.
Portuguese
Portuguese, like Spanish and French, has been heavily influenced by Latin. Portuguese has borrowed many words from Latin. The grammar of Portuguese is also influenced by Latin.
Romanian
Romanian is the only Romance language that evolved from the Latin spoken in the eastern part of the Roman Empire. Romanian has borrowed many words from Latin, such as “prieten” (friend).

Effects on English
The Roman Empire had a significant impact on English, which can still be seen today. Many words that are commonly used in English today have their roots in Latin. For example, the word “education” comes from the Latin word “educatio,” which means “a breeding, a bringing up.” Other examples include “communication,” “transportation,” and “agriculture.”
The Roman Empire also had a profound influence on the development of legal and scientific terminology in English. Latin was the language of law and scholarship for centuries, and many legal and scientific terms have Latin roots. For example, the term “pro bono” is Latin for “for the public good” and is used in the legal profession to refer to work done for free. Similarly, the term “in situ” is Latin for “in place” and is used in the scientific community to refer to something that is in its original location.
The borrowing of Latin words and the development of legal and scientific terminology are just two examples of the profound impact that the Roman Empire had on the English language.
Preservation and Transmission of Greek and Roman Literature
During the Roman Empire, the Greek language and literature were highly valued, and the Romans made efforts to preserve them. One of the ways the Romans preserved Greek literature was by translating it into Latin. For example, the famous Roman poet Virgil was heavily influenced by the Greek poet Homer and his epic poems, the Iliad and the Odyssey. Virgil’s most famous work, the Aeneid, was modeled after these Greek epics and was written in Latin.

In addition to preserving Greek literature, the Romans also made significant contributions to the transmission of Roman literature. The Roman Empire had a vast network of roads, which made it easier to transport books and manuscripts from one place to another. This facilitated the spread of Roman literature throughout the empire and, eventually, beyond its borders.
The Romans also established libraries and schools throughout the empire, which helped to spread literacy and education. The libraries contained copies of important works of literature, both Greek and Roman, which were available for scholars and students to study. The schools provided education to children of all social classes, which helped to create a more literate society. The Roman Empire played an important role in the preservation and transmission of Greek and Roman literature. Through their efforts to translate, copy, and distribute works of literature, the Romans helped to ensure that these important cultural artifacts were passed down to future generations.
The Roman Alphabet and Its Impact on Writing Systems

The Roman Empire had a significant impact on language, particularly in the development of writing systems. The Roman alphabet, which is still widely used today, was derived from the Etruscan alphabet and was introduced to Italy around the 7th century BC. The Roman alphabet consisted of 23 letters, which were used to write Latin. As the empire expanded, so did the use of the Latin alphabet, which eventually became the dominant writing system in Western Europe.
One of the key features of the Roman alphabet was its simplicity and adaptability. The letters were easy to write and could be combined to form new sounds, making it a versatile writing system. This adaptability made it easy for other languages to adopt the Roman alphabet.
The impact of the Roman alphabet on writing systems was significant, as it paved the way for the development of modern alphabets used today. The English alphabet, for example, is based on the Roman alphabet and consists of 26 letters. The use of the Roman alphabet also allowed for the standardization of spelling and grammar, making it easier for people to communicate across different regions. The Roman alphabet has had a lasting impact on writing systems, and its influence can still be seen today in the alphabets used by many languages around the world.
Modern Language Education and Classical Studies
Modern language education owes a great deal to the Roman Empire. Many modern languages, including English, French, and Spanish, have their roots in Latin. As a result, the study of Latin is still an important part of modern education.
Classical studies, which include the study of ancient Roman and Greek literature, history, and culture, are also heavily influenced by the Roman Empire. Many of the great works of classical literature were written during the Roman Empire, and they continue to be studied and appreciated today. In addition, the Roman Empire left an indelible mark on the world of art and architecture, and these influences can still be seen in modern art and architecture.
The study of classical languages and literature is not only important for understanding the history and culture of the Roman Empire, but it also provides valuable insights into the development of modern languages and literature. By studying the works of ancient writers, students can gain a deeper understanding of the human experience and the evolution of thought throughout history.
People Also Ask:
How did the Roman Empire influence language?
The influence is most notably visible in the legal sphere, where Latin-based terminology is everywhere (or, to use a Latin-based word, pervasive). Some of ancient Rome’s best-known writers were jurists and lawyers (think Cicero, Pliny, Ulpian).
How did the Romans change language?
Before the Romans arrived, there was no written language in Britain. They changed all that by teaching important Britons how to read and write and how to speak Latin. And even today, two thousand years later, a lot of our words come from Latin, like ‘enormous’ and ‘victory’ and ‘lavatory’!
How did the Romans affect the languages spoken in Europe?
Roman soldiers, colonists, and merchants took their language to many parts of Europe. Latin, the Roman language, became the spoken language across much of the western of the empire. Over centuries these languages changed into new languages such as Spanish, French, Portuguese, and Italian.
What effect did the Roman conquest have on language?
Latin became the language of conquered areas because local people started speaking it and not because the population was displaced by Latin speakers. Latin was not imposed officially on people brought under Roman rule.
Why was the Roman language important?
According to Rome’s first historian, named Virgil, Latin unified the first inhabitants of Rome together as one people. Therefore, the language was very important to the Romans, who maintained strict rules about grammar and spelling.
What is the Roman tradition in linguistics?
Roman linguistics continued studying the themes of interest to Greek linguistics and, like the other ancient traditions, was prompted by changes in the spoken language. The primary interest was in morphology, particularly parts of speech and the forms of nouns and verbs – syntax was largely ignored.
Hello, my name is Vladimir, and I am a part of the Roman-empire writing team.
I am a historian, and history is an integral part of my life.
To be honest, while I was in school, I didn’t like history so how did I end up studying it? Well, for that, I have to thank history-based strategy PC games. Thank you so much, Europa Universalis IV, and thank you, Medieval Total War.
Since games made me fall in love with history, I completed bachelor studies at Filozofski Fakultet Niš, a part of the University of Niš. My bachelor’s thesis was about Julis Caesar. Soon, I completed my master’s studies at the same university.
For years now, I have been working as a teacher in a local elementary school, but my passion for writing isn’t fulfilled, so I decided to pursue that ambition online. There were a few gigs, but most of them were not history-related.
Then I stumbled upon roman-empire.com, and now I am a part of something bigger. No, I am not a part of the ancient Roman Empire but of a creative writing team where I have the freedom to write about whatever I want. Yes, even about Star Wars. Stay tuned for that.
Anyway, I am better at writing about Rome than writing about me. But if you would like to contact me for any reason, you can do it at [email protected]. Except for negative reviews, of course. 😀
Kind regards,
Vladimir
